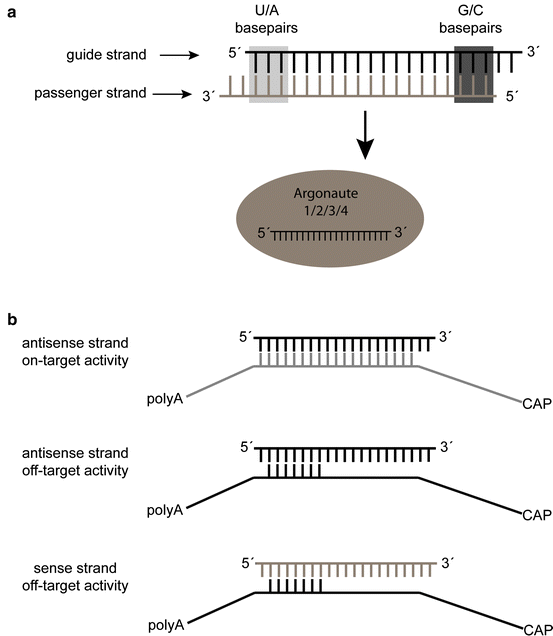
Yuan et al, 05) Thus, the seed region first identifies the target mRNAs, and subsequently form perfect basepairing with intended target mRNA and induce RNAi by Ago2Our results confirm previous reports that strength of basepairing in the siRNA seed region is the primary factor determining the efficiency of offtarget silencing However, the degree of downregulation of offtarget transcripts with shared seed sequence is not necessarily similar, suggesting that there are additional auxiliary factors that influence the silencing potential siRNA recognition of the target mRNA is conferred by the "seed region", a six nucleotide stretch corresponding to positions 27 on the antisense siRNA strand After the siRNA seed region anneals, the catalytic RNase H domain of Argonaute then subjects perfectly complementary mRNA sequences 10 nucleotides from the 5' end of the incorporated siRNA

Guidelines For The Optimal Design Of Mirna Based Shrnas Abstract Europe Pmc
Seed region of sirna
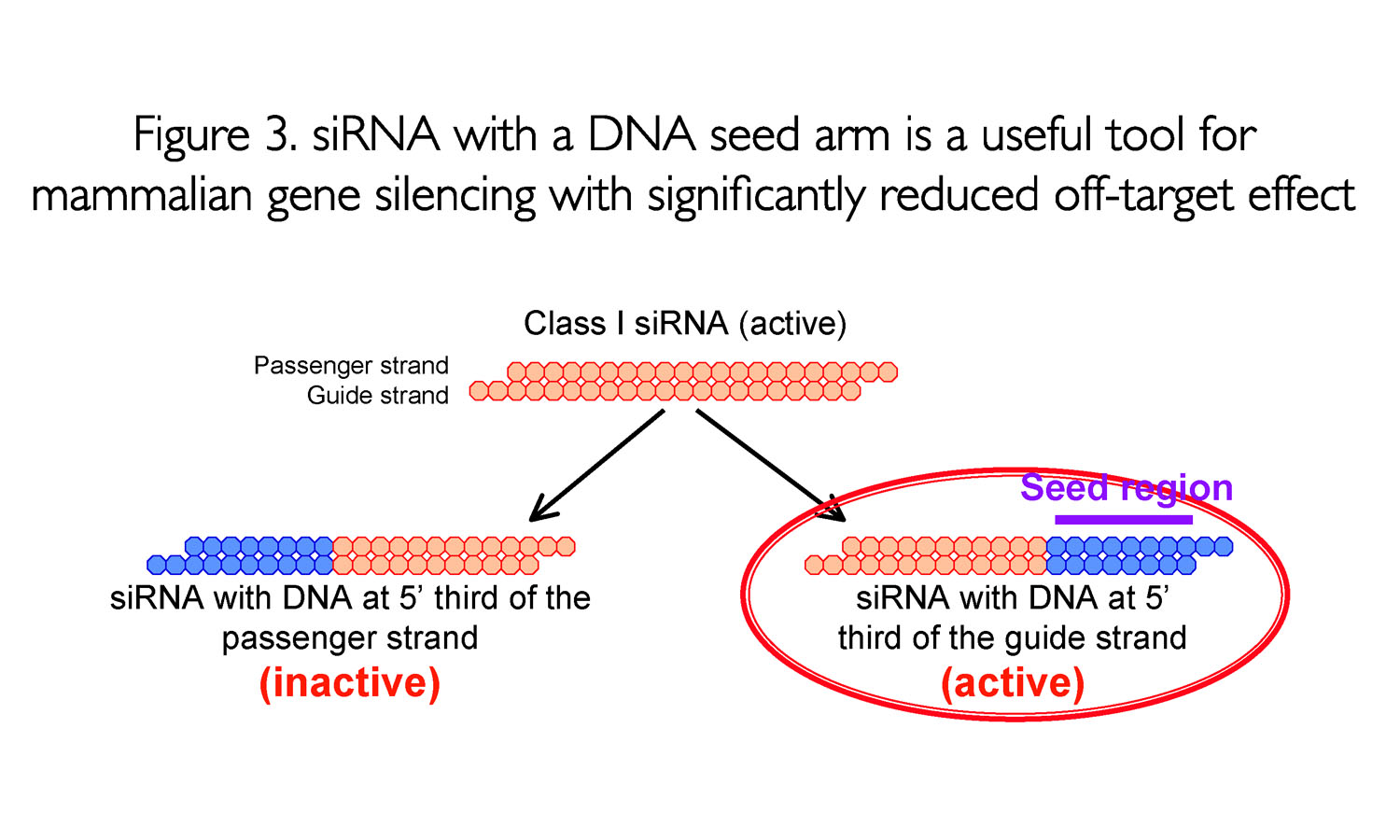
Seed region of sirna- The stability between seed region and target mRNA is a determinant of the efficacy of siRNA offtarget effects 33 Thus, the high stability of The various modifications at the 2′position of the pentose sugar of siRNA are not required for RNAi ,21 and target recognition 15 DNA is modified with hydrogen at C2′, and the 5′ onethird of each RNA strand is capable of replacement with DNA without substantial loss of RNAi activity 15 Consistent with our previous report, 15 DNA replacement at the seed region of the



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link
Previous investigations and GenScript experiment data show that siRNA "off target" transcript silencing mediated by seed region sequence is widespreed "seed region" of siRNA is analogous to seed region of microRNA GenScript resourchers found that size of seed region plays a major part in off target predictionPairing between the hexamer seed region of a small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand (nucleotides 27) and complementary sequences in the 3' UTR of mature transcripts has been implicated as an important element in offtarget gene regulation and false positive phenotypes To better understand the association between seed sequences and offtarget profiles we performedSeed region enrichment was confirmed in offtarget transcripts modulated by siRNA targeting the glucocorticoid receptor To investigate how these sites contribute to offtarget recognition of F71, we employed CXCL5 transcript as model system because it contains five F71 seed sequence motifs with single base mismatches We show by transient transfection of reporter gene
In the siRNA seed region makes it possible to overcome the sequence limitations of siRNA for reducing seeddependent offtarget effects through different molecular mechanisms reduction of basepairing stability by DNA modification, and steric hindrance by OMe modification SiRNA Modifications Avoid OffTarget Effect 19 Several recent studies suggest that the main source of siRNAmediated offtarget gene silencing could be the complementation between the 'seed' region of siRNAs (nucleotides 2–8 of theSeed region The chemical modifications of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), PS, and DNA−PS were introduced into all of the seven nucleotides of the seed region of the siRNA guide strand (Figure 2b) In addition, 3 (positions 4−6), 5 (positions 3−7),
As the offtarget effects were identified based on perfect complementarity to the seed region (positions 2–8) and both terminal nucleotides of siRNA are known to be incorporated into Ago protein (positions 1 and 21), the potential basepairing between siRNA and offtarget mRNA was determined via positions 9– (ie 3' region) The number of GC and AU basepairsSelection of Chemical Modifications in the siRNA Seed Region That Repress OffTarget Effect RNA interference mediated by small interfering RNA (siRNA) has been widely used as a procedure to knock down the expression of an intended target gene with perfect sequence complementarity However, siRNA often exhibits offtarget effects on genes with partial sequence complementaritiesFAQ ID 2262 miRNAs regulate the gene expression by binding to the mRNA The seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed




6mer Seed Toxicity Determines Strand Selection In Mirnas Biorxiv
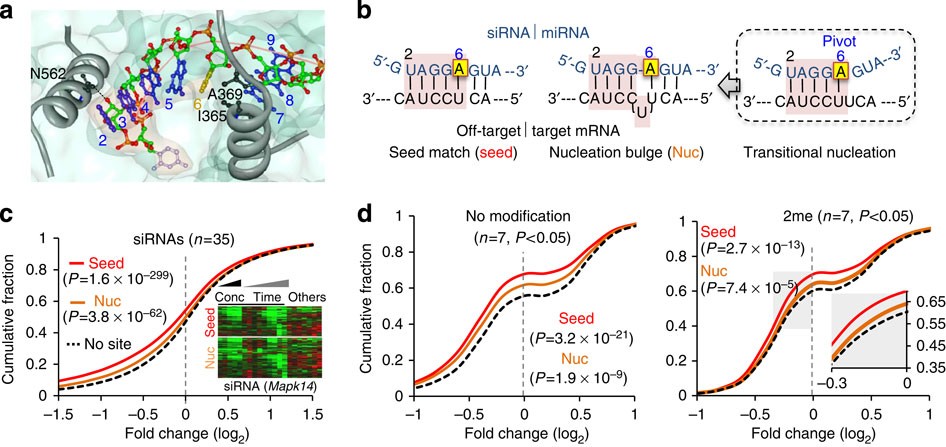



Abasic Pivot Substitution Harnesses Target Specificity Of Rna Interference Nature Communications
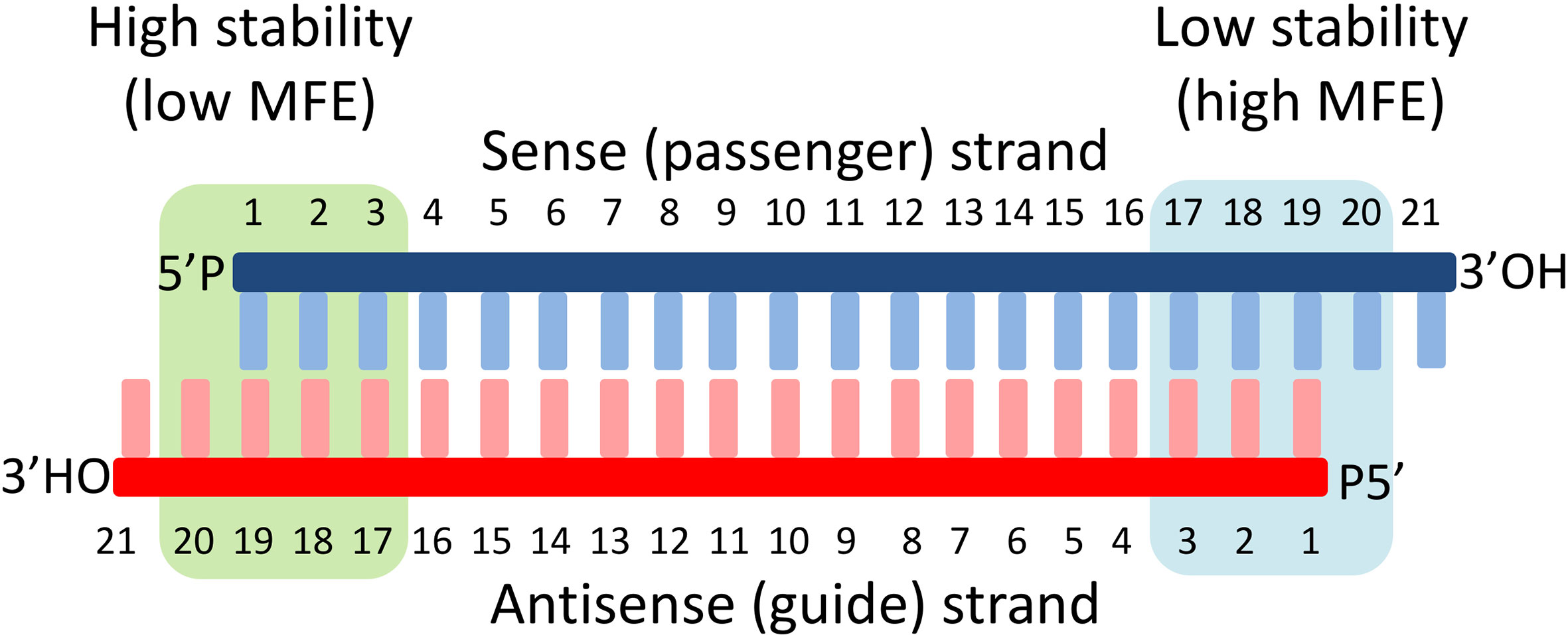
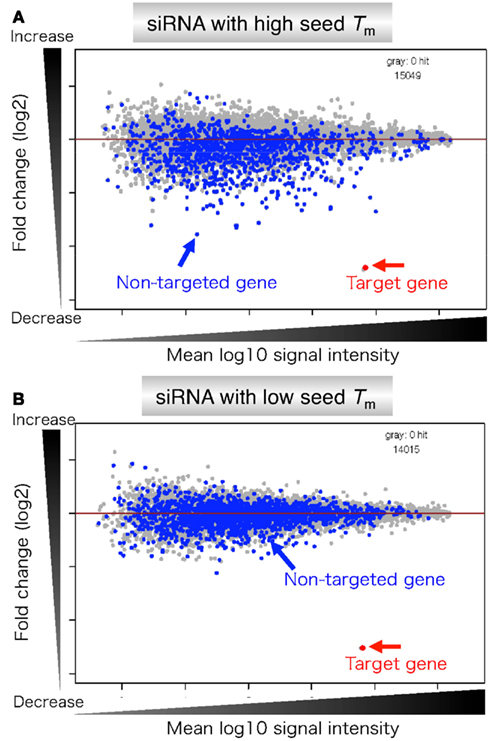
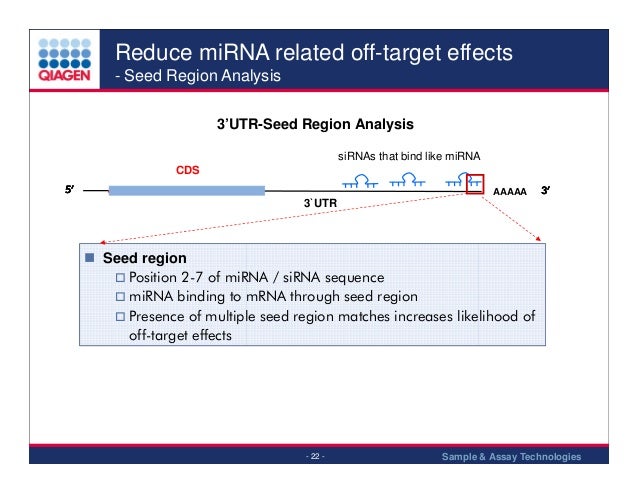
The seed region comprises 6 nucleotides in positions 2–7 of the antisense siRNA strand of the siRNA duplex Matches such as these can contribute to downregulation of unintended targets due to the siRNA mimicking the action of an miRNA siRNA designed at QIAGEN is analyzed for 3' UTR/seed region complementarity using a proprietary set of 3' UTR sequences derived from theIn addition, it is clear that unintended genes with complementarities only in the seed region (positions 28) are also downregulated by offtarget effects siRNA efficiency is mainly determined by the WatsonCrick basepairing stability formed between the siRNA seed region and target mRNA siRNAs with a low seedtarget duplex melting temperature (T(m)) have little or no seedThe seed region is known to be situated on the surface of Ago in a quasihelical form to serve as the entry or nucleation site for small RNAs in the RISCs (Ma et al, 05;



1




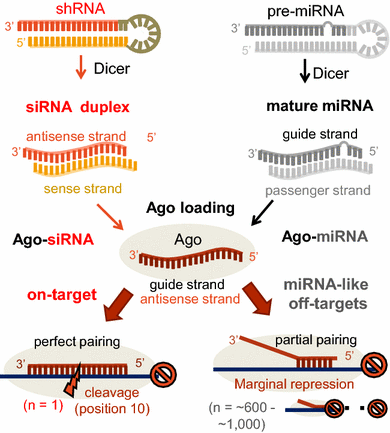
Passenger Strand Cleavage Facilitates Assembly Of Sirna Into Ago2 Containing Rnai Enzyme Complexes Cell
Lane 1, siRNA with a dsDNA seed duplex Lane 2–lane 13, siRNA with a dsDNAmodified seed duplex and two additionally DNAsubstituted base pairs in the nonseedduplex region DNA substitutions at positions 13 and 14 and of the 3′ overhang of the guide strand changed little, if any, RNAi activity (lanes 6, 12, 13)Chemical modifications of 2'Omethyl (2'OMe) and locked nucleic acid (LNA) of the nucleotides in the seed region (positions 28) of the small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand significantly reduced seedmatched (SM) offtarget effects The siRNA
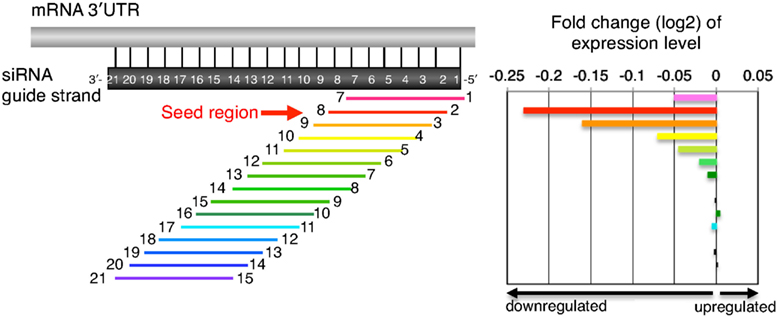



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics




Shrna And Sirna Of The Same Sequence Regulate The Same Subset Of Download Scientific Diagram




Figure 3 Specific Silencing Of L392v Psen1 Mutant Allele By Rna Interference




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database
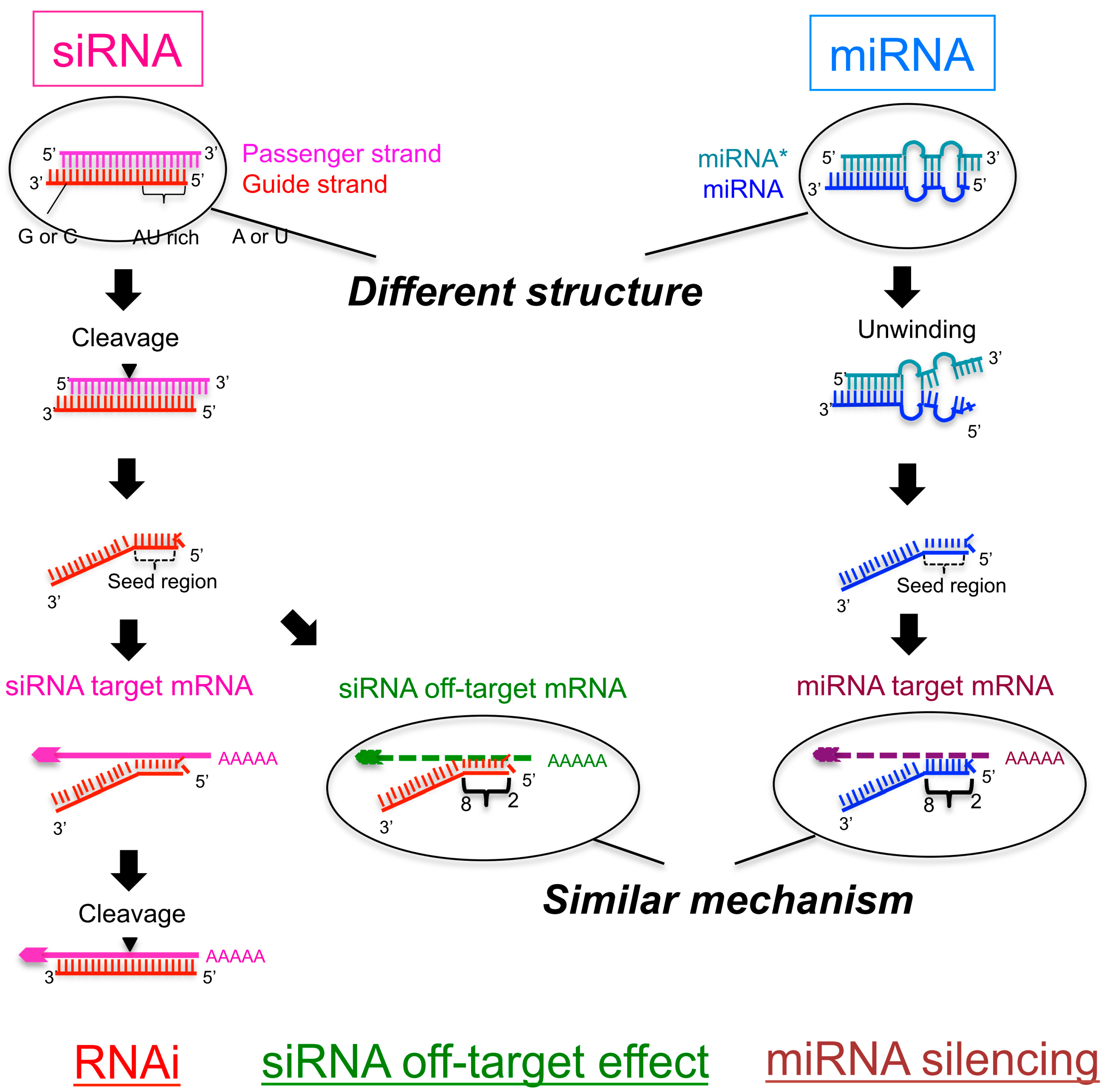



Ijms Free Full Text Is The Efficiency Of Rna Silencing Evolutionarily Regulated Html
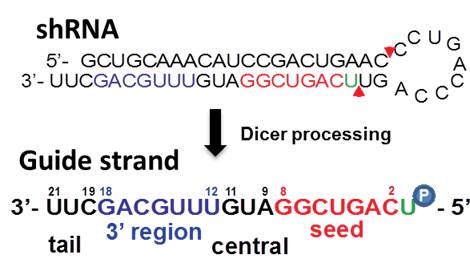



Sirna Shrna Oligo Optimal Design



Frontiers Sirna Finder Si Fi Software For Rnai Target Design And Off Target Prediction Plant Science



2




A The Structure Of Sirna Sense And Antisense Strands And Target Mrna Download Scientific Diagram




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



Sirna Design Principles And Off Target Effects Springerlink



2




At Enrichment In Both Seed And 3 Regions Is An Optimal Design To Download Scientific Diagram




Modification Of The Sirna Passenger Strand By 5 Nitroindole Dramatically Reduces Its Off Target Effects Zhang 12 Chembiochem Wiley Online Library



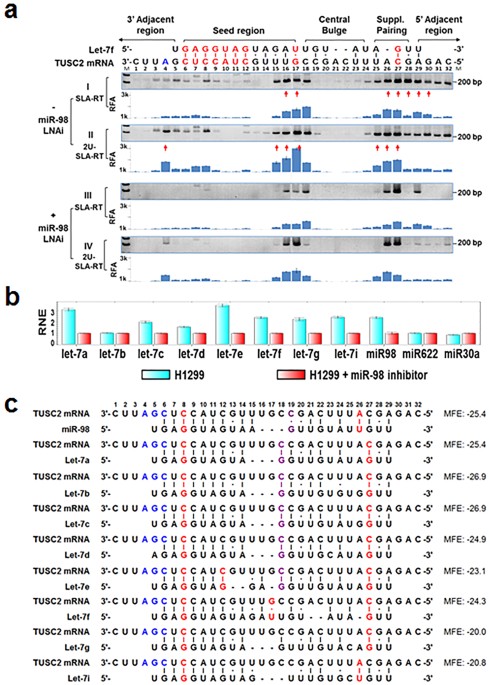
The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects Document Gale Academic Onefile




Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database



Specific Sirna Effect Left And Sirna Off Target Effects In Which Download Scientific Diagram
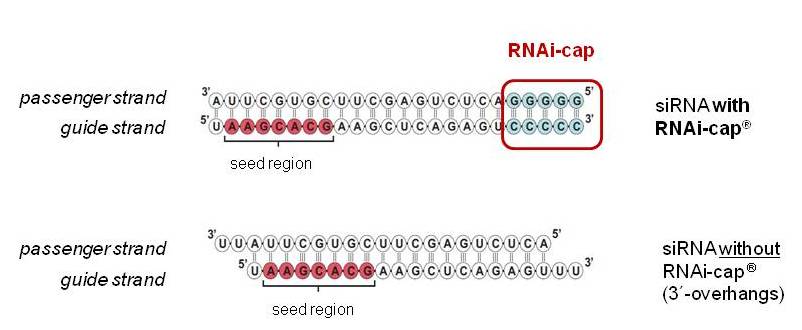



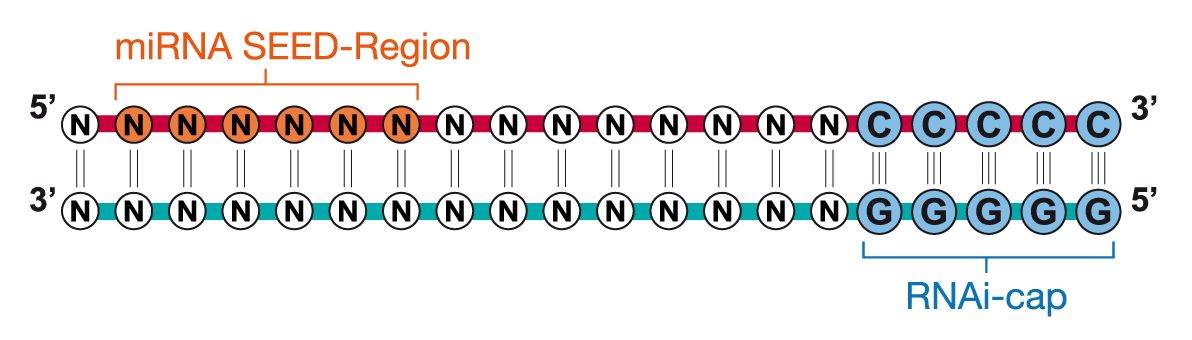
Riboxx Rna Technologies Better Silencing With Rnai Cap



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics



Gess




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal



Frontiers Synthetic Rnas For Gene Regulation Design Principles And Computational Tools Bioengineering And Biotechnology




Seed Based Off Target Effects In Pooled Sirna Screens A An On Target Download Scientific Diagram




Sirnas And Shrnas Tools For Protein Knockdown By Gene Silencing



Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text Disease Causing Allele Specific Silencing By Rna Interference Html




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Sciencedirect



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects



1




An In Silico Analysis Of Effective Sirnas Against Covid 19 By Targeting The Leader Sequence Of Sars Cov 2 Pandey 21 Advances In Cell And Gene Therapy Wiley Online Library



2



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram




Clinical Development Of Synthetic Sirna Therapeutics Sciencedirect




Alleviation Of Off Target Effects From Vector Encoded Shrnas Via Codelivered Rna Decoys Pnas




Pdf Interfering With Disease A Progress Report On Sirna Based Therapeutics Semantic Scholar




Rational Design Of Therapeutic Sirnas Minimizing Off Targeting Potential To Improve The Safety Of Rnai Therapy For Huntington S Disease Sciencedirect



Pubs Rsc Org



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Expression Dynamics Of Mirnas And Their Targets In Seed Germination Conditions Reveals Mirna Ta Sirna Crosstalk As Regulator Of Seed Germination Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And




Seed Dependant Off Target Effect The Capability Of Sirnas To Induce Download Scientific Diagram



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link



Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo




Selective Targeting Of Point Mutated Kras Through Artificial Micrornas Pnas




Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo



Si Rna 13




Tolerance For Mismatches Between An Sirna And Its Target Sirna Seed Download Scientific Diagram




Pdf Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar



Microrna Mediated Target Mrna Cleavage And 3 Uridylation In Human Cells Scientific Reports




Current Status For Application Of Rna Interference Technology As Nucleic Acid Drug Intechopen




Pdf New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens Semantic Scholar




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




Functional Sirna Sequence And The Mechanism Of Rnai Without Off Target Download Scientific Diagram




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



Evaluation And Control Of Mirna Like Off Target Repression For Rna Interference Springerlink




Gene Silencing By 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Modified Sirna A Prodrug Type Sirna Responsive To Reducing Environment Sciencedirect
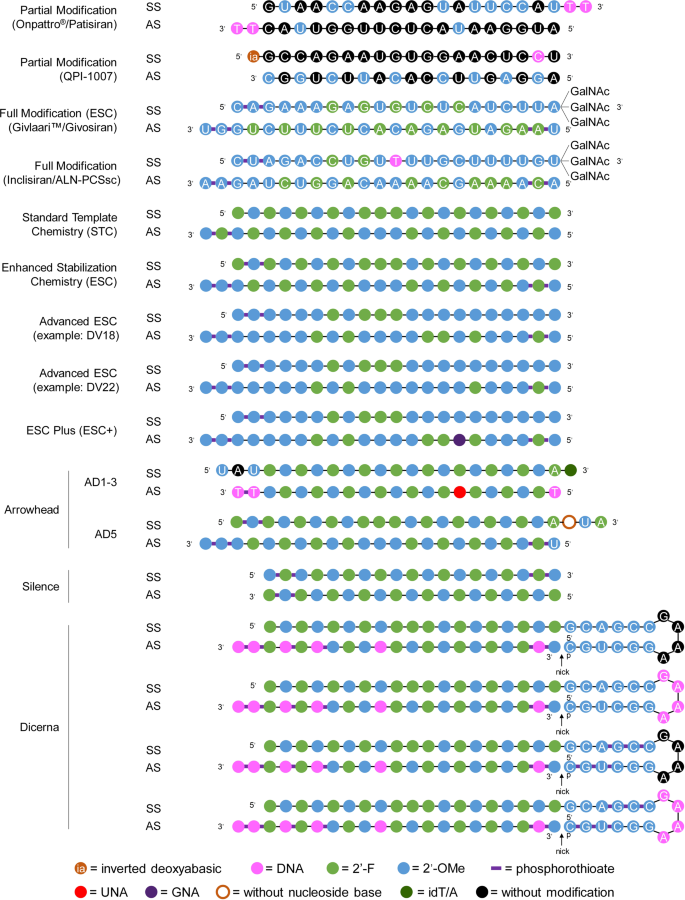



Therapeutic Sirna State Of The Art Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database
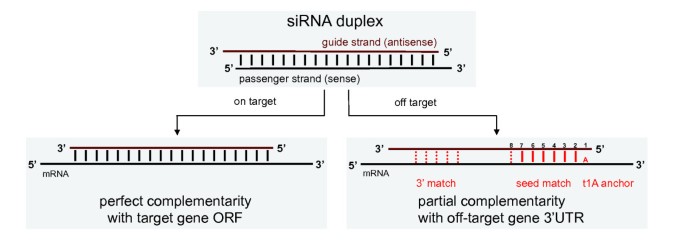



Off Target Effects Dominate A Large Scale Rnai Screen For Modulators Of The Tgf B Pathway And Reveal Microrna Regulation Of Tgfbr2 Silence Full Text



2
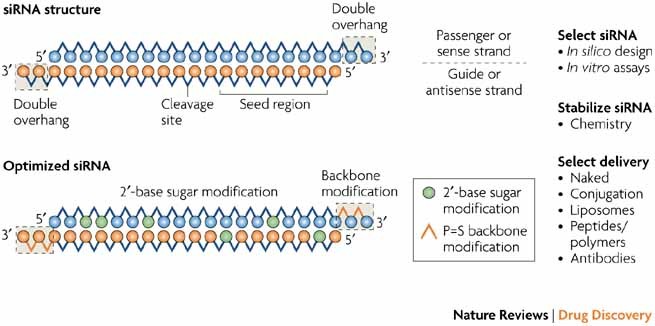



Interfering With Disease A Progress Report On Sirna Based Therapeutics Nature Reviews Drug Discovery




Sidesign Center User Guide
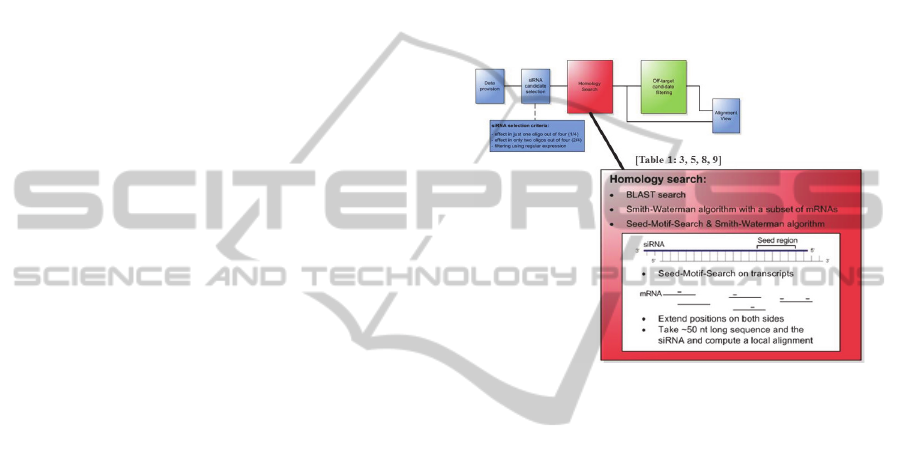



New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens




Figure S1 Schematic Representation Of Amirna Vs Sirna Approach A Download Scientific Diagram




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
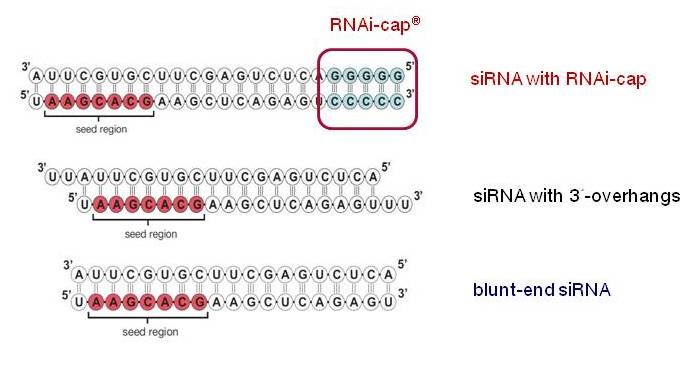



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna
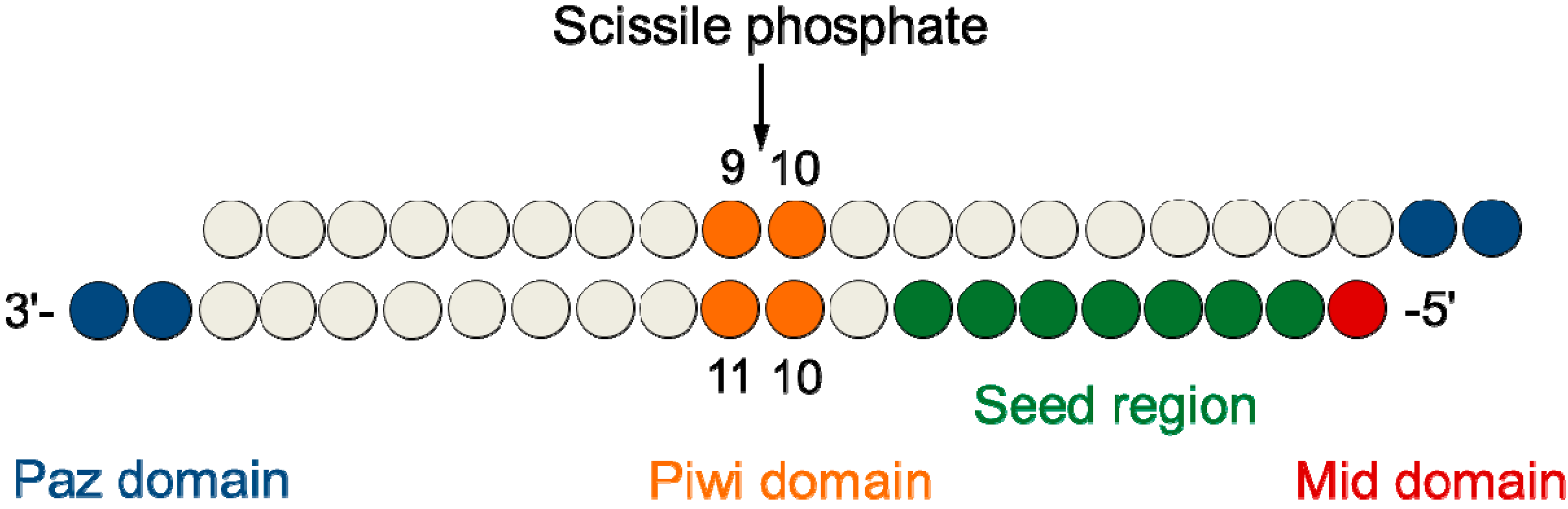



Molecules Free Full Text Modulation Of The Rna Interference Activity Using Central Mismatched Sirnas And Acyclic Threoninol Nucleic Acids Atna Units Html
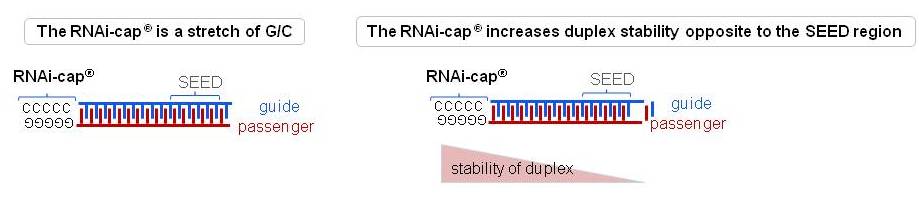



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna



Sidirect




Graphical Representation Of Sirna Molecule A Sirna Duplex With Download Scientific Diagram




Effective Gene Silencing Activity Of Prodrug Type 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Sirna Compared With Non Prodrug Type 2 O Methyl Sirna Sciencedirect



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Guidelines For The Optimal Design Of Mirna Based Shrnas Abstract Europe Pmc
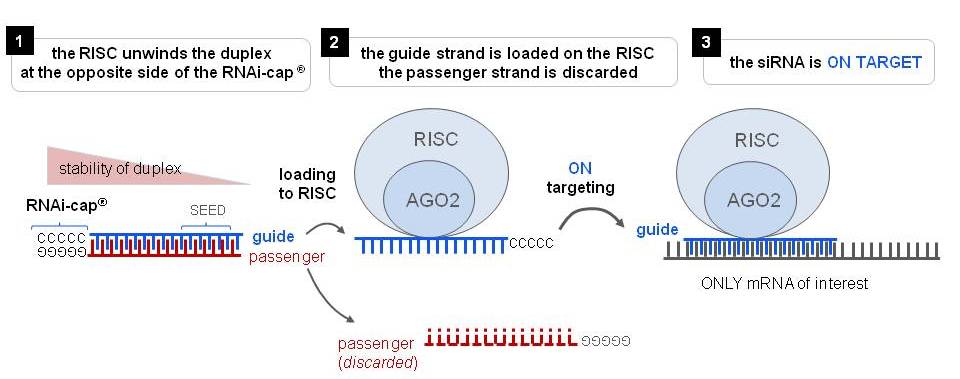



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna




Selection Of Chemical Modifications In The Sirna Seed Region That Repress Off Target Effect Springerlink




Reduced Seed Region Based Off Target Activity With Lentivirus Mediated Rnai
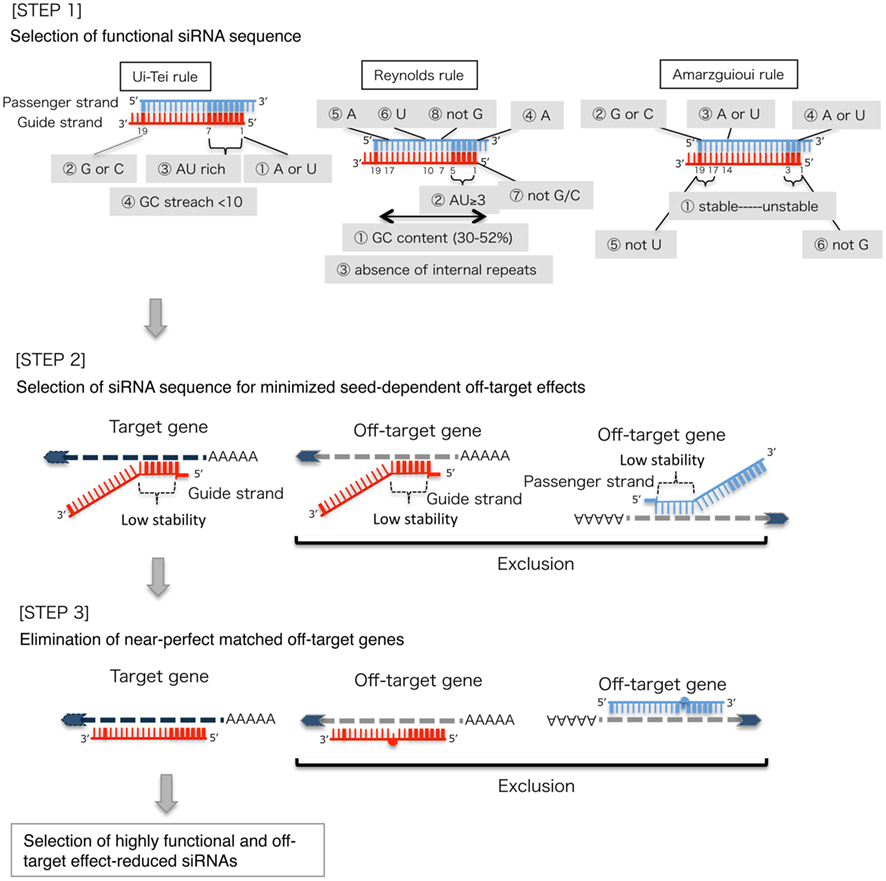



Frontiers Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Genetics
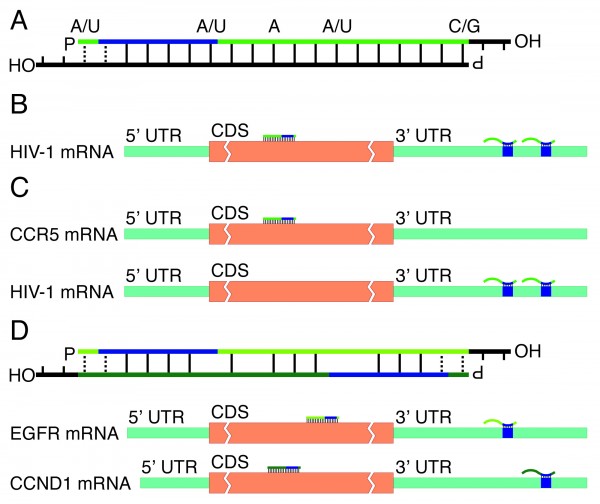



Unconventional Rna Interference Recent Approaches To Robust Rnai European Pharmaceutical Review




Abundant Expression Of Maternal Sirnas Is A Conserved Feature Of Seed Development Pnas




Cell Free Reconstitution Reveals The Molecular Mechanisms For The Initiation Of Secondary Sirna Biogenesis In Plants Pnas



1
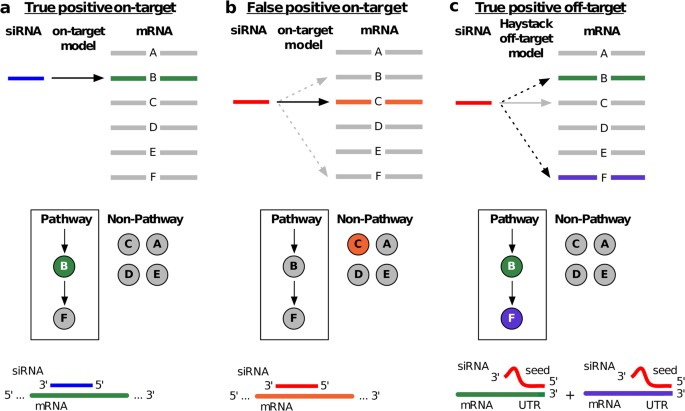



Sirna Off Target Effects In Genome Wide Screens Identify Signaling Pathway Members Scientific Reports



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects



2
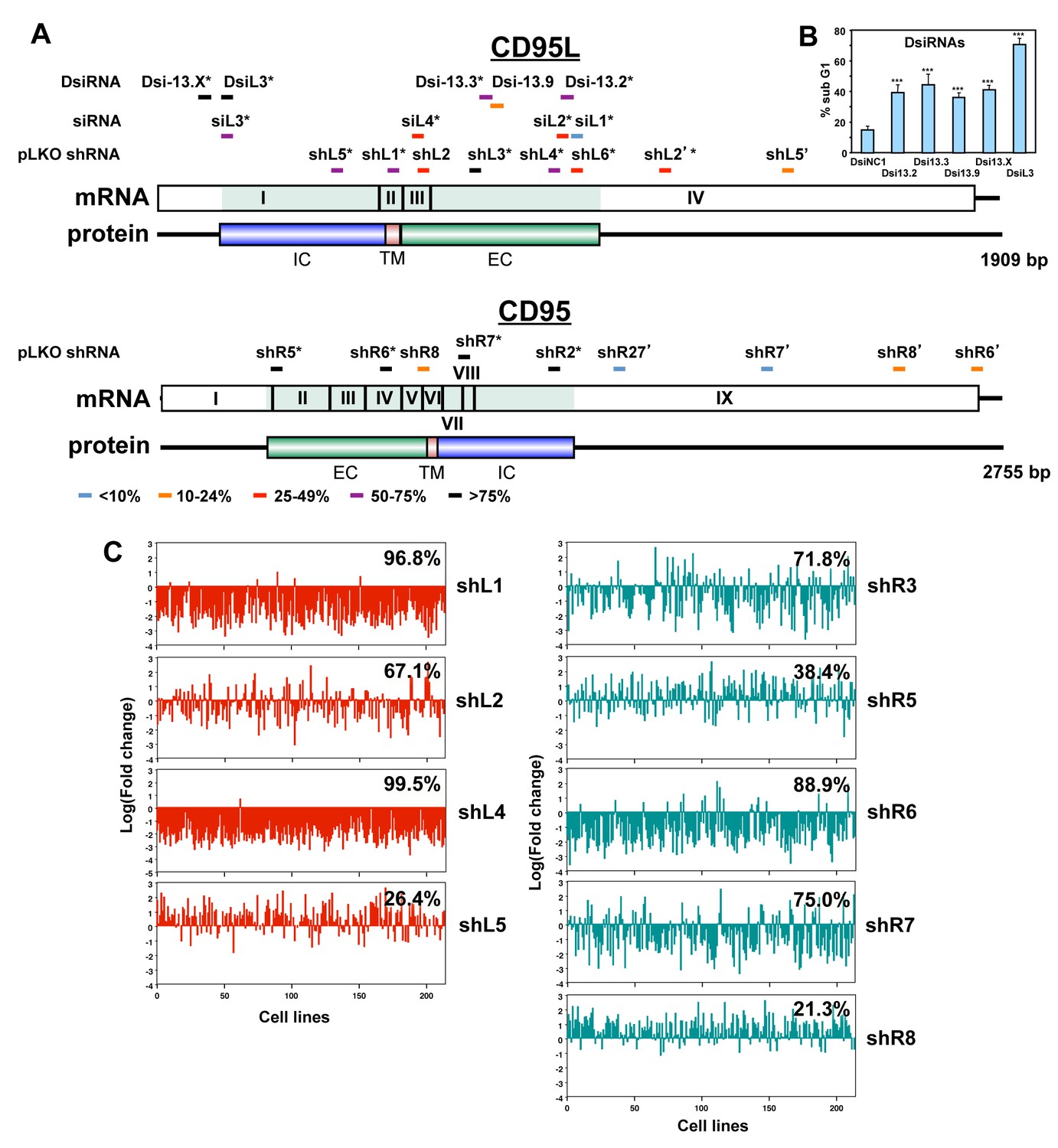



Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram




Effective Gene Silencing Activity Of Prodrug Type 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Sirna Compared With Non Prodrug Type 2 O Methyl Sirna Bioorganic Medicinal Chemistry Letters X Mol



Part a K Parts Igem Org




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




Effects Of Dna Substitutions In The Non Seed Duplex Subdomains A B C Download Scientific Diagram




A Simple And Cost Effective Approach For In Vitro Production Of Sliced Sirnas As Potent Triggers For Rnai Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
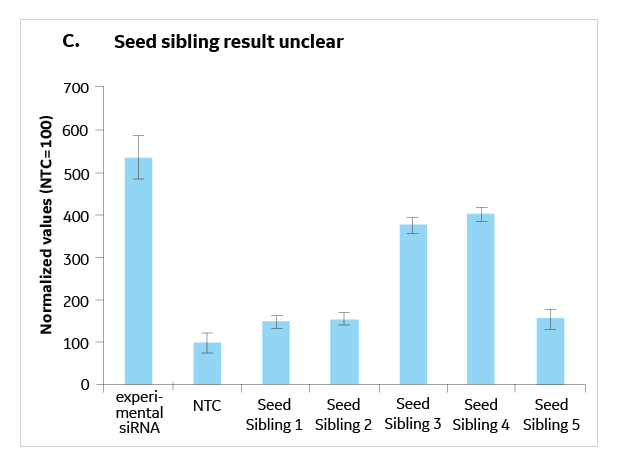



Seed Sibling Controls For Rnai Hit Validation
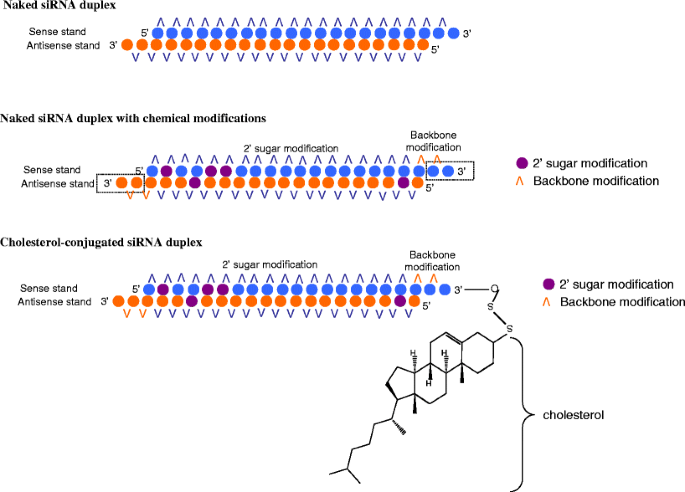



Rnai For Treating Hepatitis B Viral Infection Springerlink
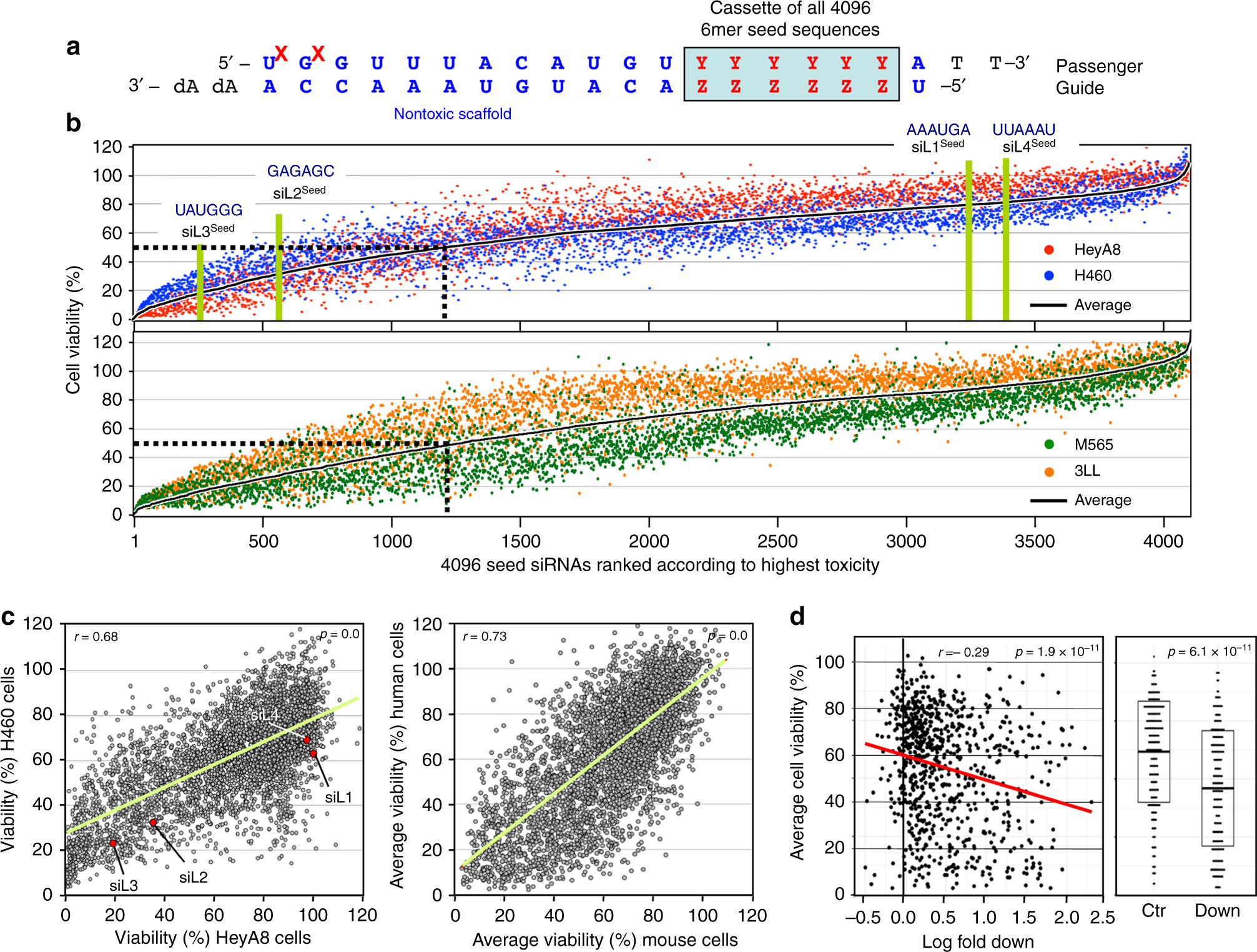



6mer Seed Toxicity In Tumor Suppressive Micrornas Nature Communications




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram



1



No comments:
Post a Comment